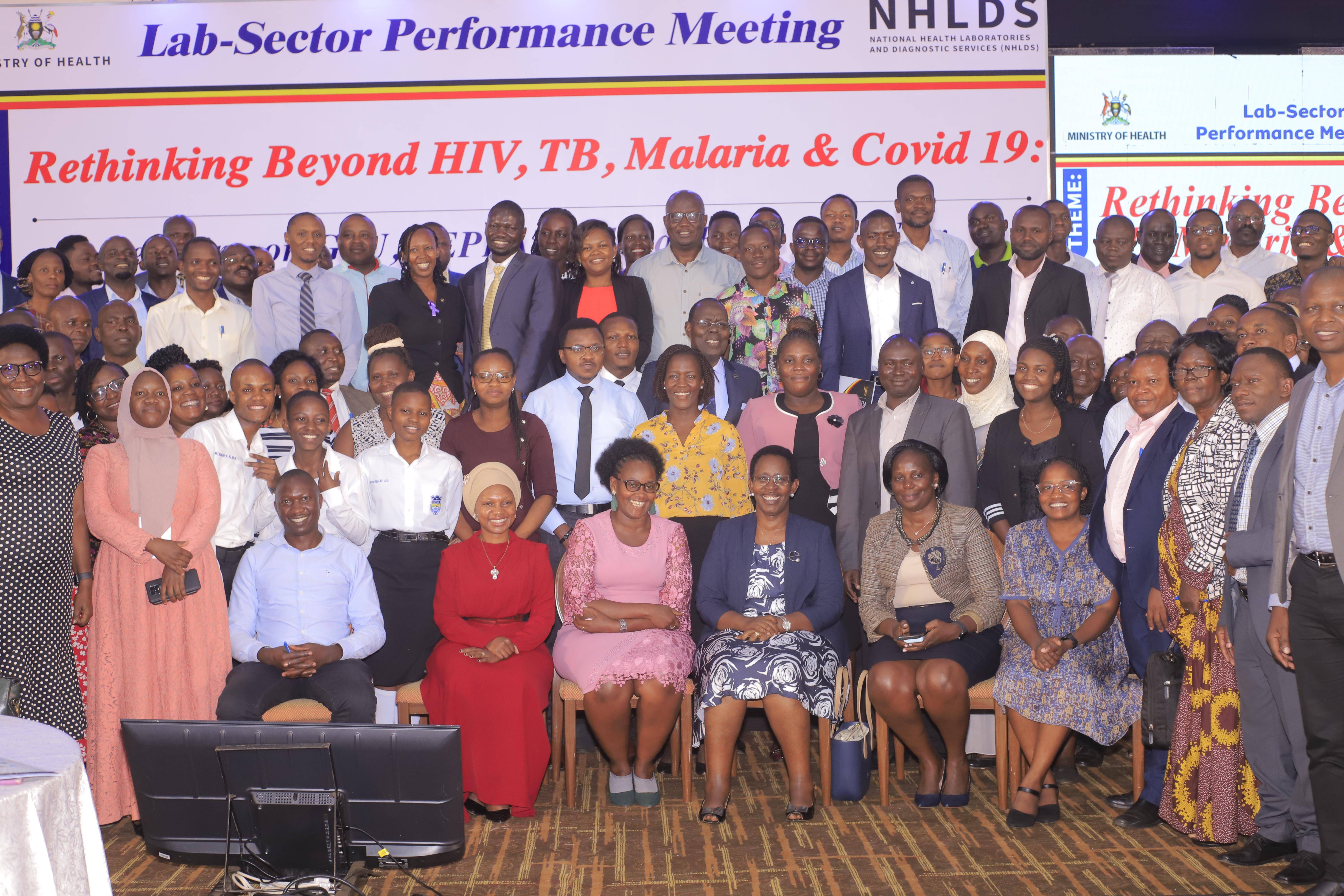
Uganda’s Health Laboratory and Diagnostic Sector Surges Forward
Kampala- 28th September, 2023
"The Laboratory Sector is making significant strides," said Dr. Diana Atwine, the Permanent Secretary of the Ministry of Health, while she officiated at the Laboratory and Diagnostic Sector performance review meeting held at Hotel Africana.
This statement underlines the remarkable growth witnessed in the Laboratory and Diagnostic sector of Uganda over the years.
The meeting revolved around the theme, "Rethinking Beyond HIV, TB, Malaria, and COVID-19: Leveraging on PEPFAR and Global Fund platforms to shape a new landscape for sustainability." It was an opportunity to evaluate the performance and progress of laboratory and diagnostic services in the country.
During the event, Dr. Susan Nabadda, the Commissioner of the National Health Laboratory and Diagnostic Services (NHLDS) delivered a presentation that highlighted the significant progress made within the sector, achievements, its potential for growth, partnerships, and the challenges it currently faces.
"We have witnessed substantial improvements in various aspects of laboratory and diagnostic services, The Laboratory and Diagnostic sector in Uganda has undergone a transformative journey in recent years. We've seen remarkable strides in our ability to provide critical healthcare services to our citizens, extending far beyond our initial focus on HIV, TB, Malaria, and COVID-19." Dr. Nabadda.
She went on to provide specifics on the sector's accomplishments, which included advancements in disease testing, research, and healthcare delivery.
Dr. Nabadda also shed light on the numerous opportunities for growth within the Laboratory and Diagnostic sector. "There are significant opportunities for expansion and development in this sector. Our commitment to leveraging platforms such as PEPFAR and the Global Fund has been instrumental in driving our success. These partnerships have not only enabled us to tackle major health crises effectively but have also laid the foundation for a more sustainable and adaptable healthcare landscape," she emphasized.
These opportunities encompass areas such as technology integration, capacity building, and increased collaboration with international organizations.
However, the Laboratory Sector is not without its fair share of challenges. Dr. Nabadda acknowledged that the sector faces several obstacles that need to be addressed for sustained growth. "We must overcome challenges related to funding, infrastructure, and the availability of skilled personnel," she noted.
Below are the key highlights of Dr, Nabadda’s presentation on the performance of the sector;
-
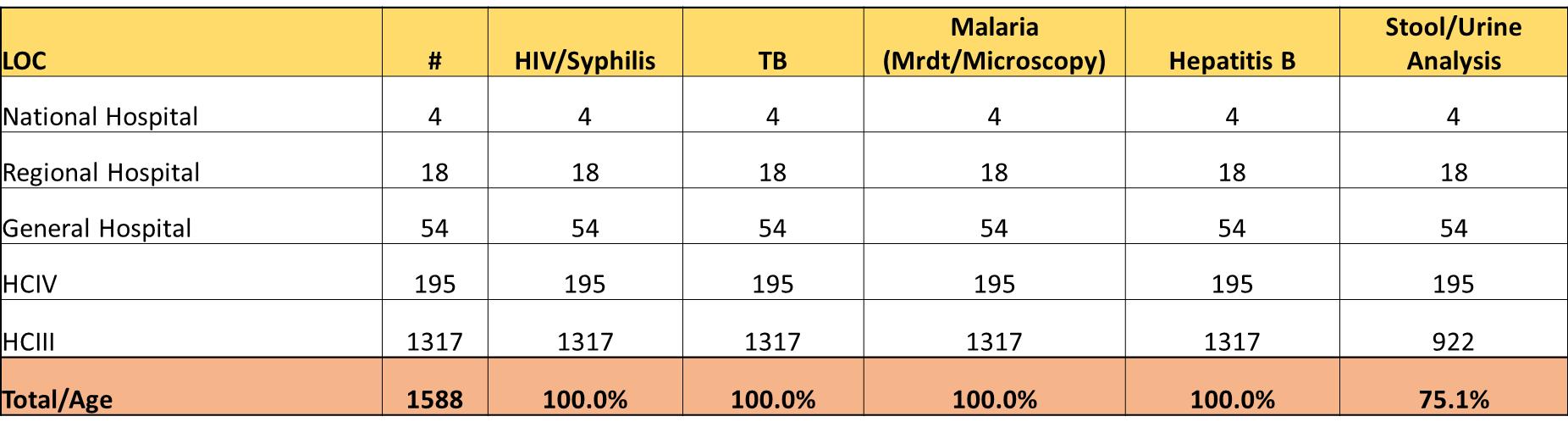
Laboratory Testing Capacity in the country.
-
295 GeneXpert machines across the network being used for testing TB, HIV Viral Load, EID, HPV and COVID-19. Additional 40 Truenat machines and 17 TB LAMP were added in the network to support TB testing.
-
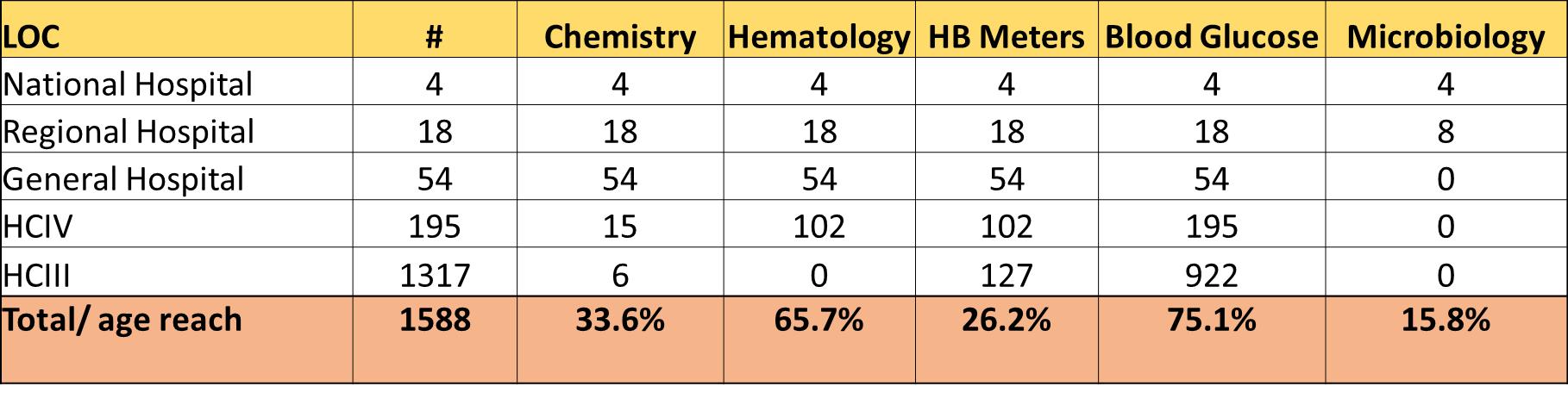
There are 105 and 145 HFs with capacity to test Chemistry and hematology at different levels of care across the country. By 2024, all 271 HFs will have capacity to test chemistry and hematology tests across the country.
-
1,000 HB meters have been distributed in 452 HFs across the country to support HB testing in ANC and Blood transfusion Labs.
-
All 1588 HFs were supplied with Glucometers to support rapid blood sugar screening for NCDs.
-
15 RRHs were provided with automated blood transfusion Equipment to improve on the quality of blood transfusion services.
-
10 RRHs have automated microbiology equipment with Masaka RRH being fully automated with capacity to perform microbiology tests
-
We however lack Histopathology equipment to support cancer diagnosis at RRH
-
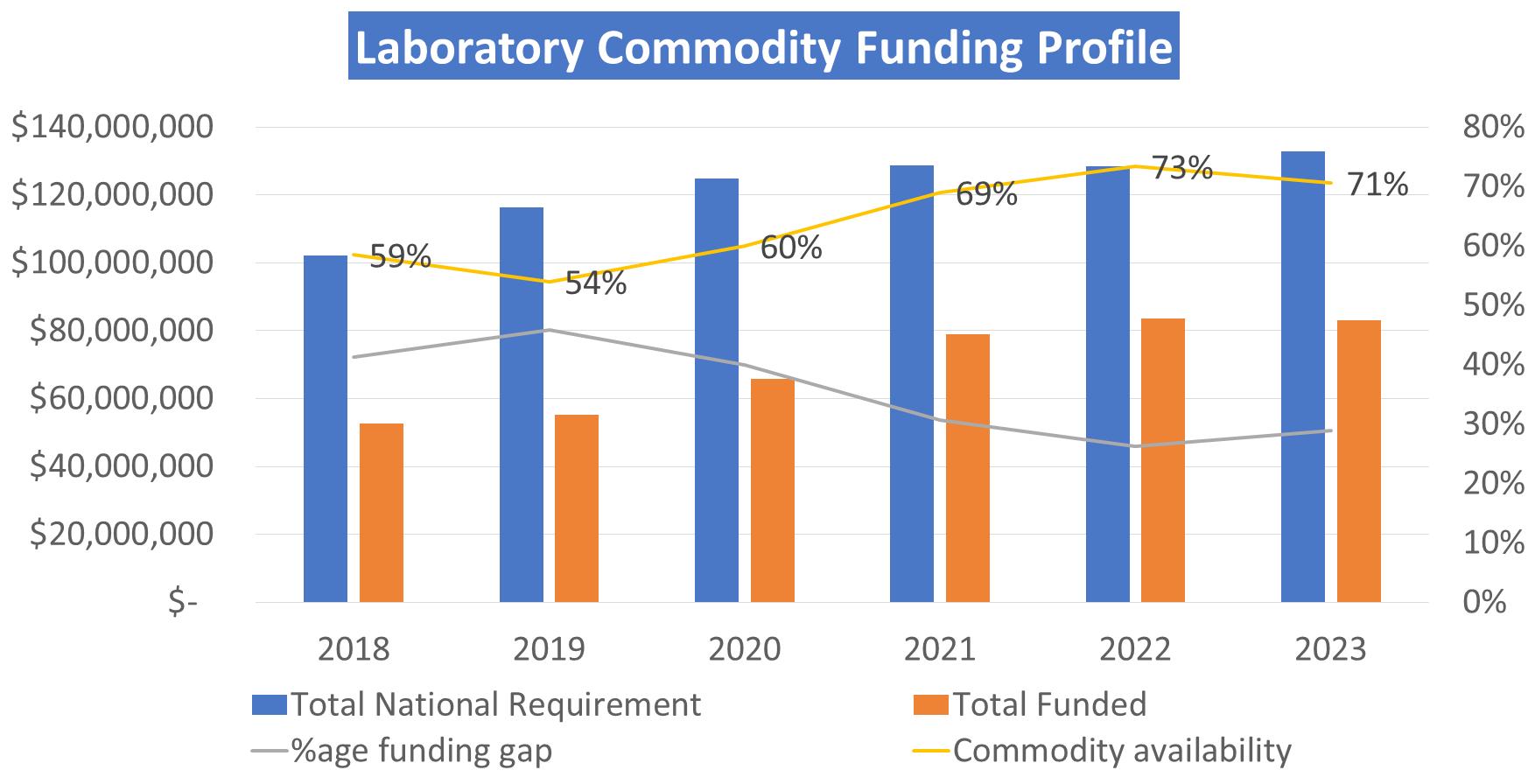
Commodity Funding:
With increased funding of Laboratory commodities, the commodity availability has increased to 70% in 2023 from 59% in 2018. However, the funding of Laboratory commodities is still limited leading to an average of 28% stock out of supplies across the network.
Also note increased commodity funding requirement over years due to growing laboratory scope.
-
Centralized Reference Testing.
High Throughput:
-
HIV Viral load- 7000 tests/day
-
EID- 200 tests/day
-
Leverage capacity for multiplexing;
-
Hepatitis
-
HPV
-
COVID
-
-
Rapidly Detected and Responded to Bacterial Disease out breaks in 8 Districts; Cholera, Dysentery, Neisseria Meningitidis and suspected cases with food poisoning.
-
Sickle Cell Disease Program:
-
52,148 new born babies have been screened of which ~2% (1,042) had Sickle cell Disease
-
The new born screening capacity at the lab is 15gels (1,200 test) per day, 26,440 a month and 316,800 per year.
-
Non Communicable diseases
We are stepping up the capacity in NCD testing & diagnosis through early detection, monitoring, diagnosis for quality patient management leveraging on the investments for infectious disease.
-
HTN – LFTs, RFTs, Urinalysis, CBC, lipid profile
-
Diabetes – RFS, FBS, Urinalysis, HBA1C
-
Mental health conditions; depression, anxiety, substance abuse
-
Drug and substance abuse- LFTs, RFTs, Cortinin and others
-
Screening for Cancer cervix, Colon, Prostate – CEA,HPV,PSA
-
Currently integrating NCD into HIV care – HPV testing, Hb A 1c
-
A-LIS- implementation in RRH, GH, HCIV, machine interface, working on integration with EMR (Clinic Master and eAFYA ) and ALIS Data warehouse.
-
Biosafety /Biosecurity: NHLDS works in collaboration with other MDAs to implements the risk-based Biosafety Biosecurity across the Human, animal, Water and Environment facilities.
-
Improved Lab Infrastructure at National and subnational levels have improved access to quality laboratory services.